The segment on chromosomes that produce traits are called what?
What are alleles?
This gene always shows itself over a recessive gene
What is a dominant gene?
What does it mean when something is following the law of Dominance?
The dominant allele will always be expressed over the recessive allele.
What is it called when neither the dominant nor the recessive trait can overpower the other and you get a blending of the two traits?
What is called incomplete dominance?
What percent of offspring will be homozygous dominant?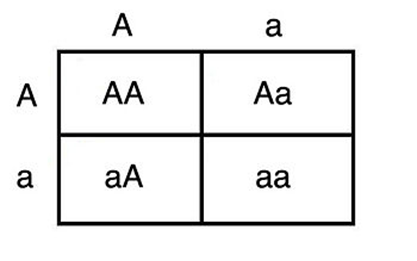
What is 25%?
The passing of traits from parent to offspring is called.
What is heredity?
Organisms that have two of the same genes
What is homozygous?
Type of cell division that helps create the sex cells needed for genetics to be studied?
What is meiosis
What is it called when a gene needs more than one allele in order to be expressed? (Hint think of blood type)
what is multiple alleles?
What percent of the offspring of heterozygous parents will be homozygous recessive?
What is 25%?
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA that is responsible for making proteins.
Organisms have two different genes for the same trait.
what is heterozygous?
One of Mendel's laws was the law of segregation, what did this law mean for chromosome distribution?
It meant that in meiosis each gamete will receive only one chromosome from each pair.
When we have both traits are dominant and they both get showed by the organism. What is this principal called?
What is codominance?
Perform a cross of two people who have the following blood types. The father has AB blood and the mother has BO blood. After doing the cross what would be the possible blood types their offspring would have (A, B, AB. or O)?

What is the meaning of Homologous Chromosomes?
These are chromosomes that are the same shape, same size, and same locations of genes.
Shows possible gene combinations for only one trait.
What is a monohybrid cross?
If an individual is a heterozygous for the trait of eye color and brown is the dominant trait. What would this person's eye color be and what would their genotype look like if we were to use the letter "b"?
The person would have brown eyes.
Their genotype would be Bb.
What is it called when genes are physically located on the same chromosome and have a very high likely hood of being inherited together? (Hint: think of blond hair and blue eyes)
What is called linked genes?
Below you will find a dihybrid cross. The cross below is of two homozygous birds, where Curved beaks (B) is dominant to straight beaks. Then, Blue feathers (F) is dominant to red feathers. How many of the offspring would have straight beaks and blue feathers? What would that be as a percent?
What is 8 birds and 50%?
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype.
Genotype= the written alleles from the chromosomes
Phenotype= The physical traits (A.K.A. what you can see)
What is the cross called for when you want to look at two traits? Then how many possibilities does this cross give you in?
A dihybrid cross will show the probability of two traits.
This type will give you 16 different possibilities.
The last of Mendel's laws was the law of independent assortment, what did this mean for chromosome distribution and what did it help to increase within sexually reproducing organisms?
The assort meant of chromosomes was at random and they did not influence each other.
It helped increase genetic diversity.
This type of inheritance produces a range in the phenotypes showed by the organisms and is displayed by using a bell curve. What is the name of this type of inheritance and provide me with an example of a trait for humans that follows this type of inheritance.
What is polygenic inheritance?
Those examples could be height, skin color, and eye color.
A father who is colorblind and his wife has members of her family who are colorblind want to find out their children's chances of getting the disease. Colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. Make a cross for the following problem. Then, conclude will they have a child who is color blind? Second, if so, what gender would they be?

Yes
One of them will be female and one will be male.
